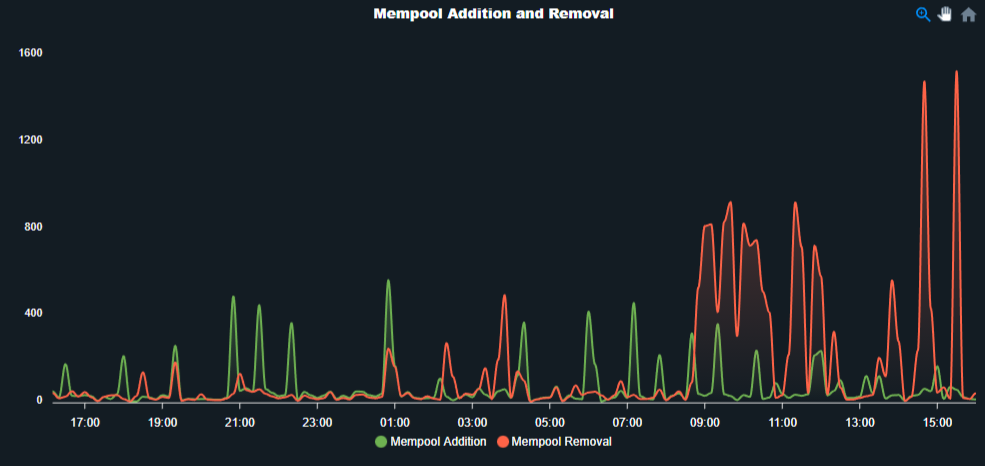
Mempool
-
A memory pool is simply a "waiting room" that holds the unconfirmed transactions.
-
One of the most prominent uses of the Mempool is to get pending transactions.
-
When a node receives a transaction, it will propagate the transaction to peer nodes until a farmer approves the transaction and adds it to a new block.
-
As the transaction move from mempool to the farmers, they are sorted and processed according to profitability.
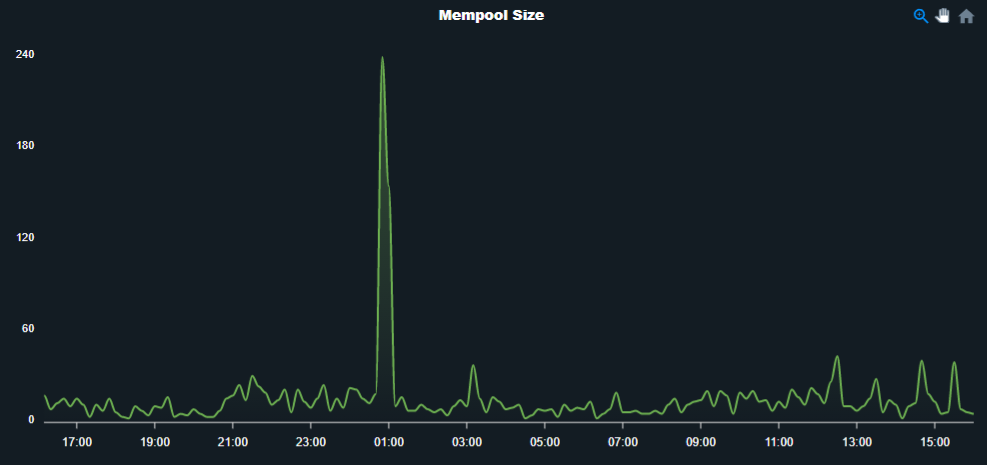
1. Mem size
-
It is the number of transactions in mempool to,that is to be processed.
-
A high mempool size indicates more network traffic which result in higher priority fees.
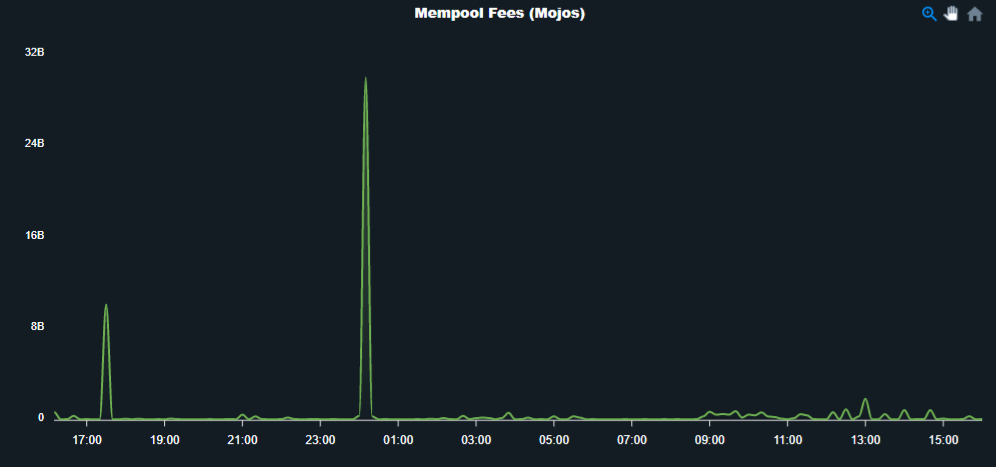
2. Mem fee
-
It shows how much people paying for the transaction.
-
If mempool is not full, It will accept all transactions regardless of fees.
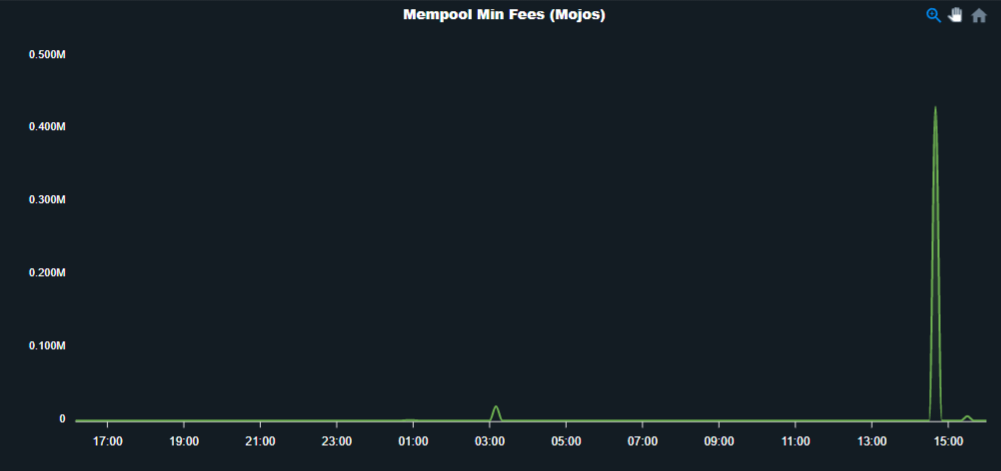
3. Min fee
-
It is the minimum relay fee for the mempool when the mempool gets too big.
-
When mempool becomes full it will start rejecting or it will not accept any more transactions.
4. Addition
-
It is the total number of mempool added to the queue.
-
After a new block added to the blockchain, all full nodes check out the coins that are spent and remove them from mempool.